BIRDS FROM SIMA DEL ELEFANTE, ATAPUERCA, SPAIN: PALAEOECOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS IN THE OLDEST HUMAN BEARING LEVELS OF THE IBERIAN PENINSULA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.13130/2039-4942/16027Keywords:
Aves; early Pleistocene; Europe; human occupation; Imperial eagle; Corvus pliocaenus.Abstract
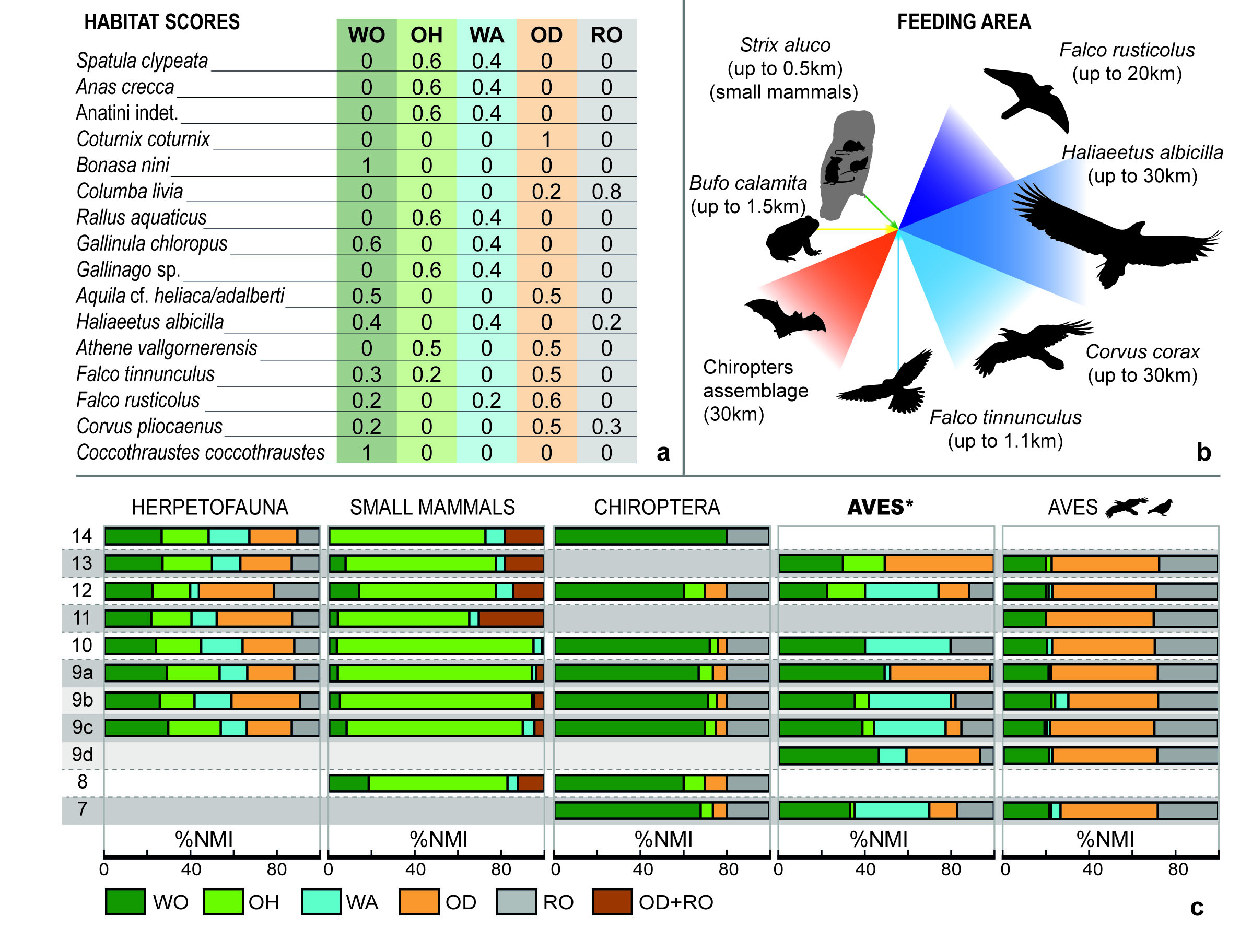
Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of early Pleistocene sites has a particular interest as it sheds light on how the arriving of the first Europeans occurred, as well as on the nature of the relation between these humans and the ecosystems. Bird remains are useful tools for this purpose, because they are commonly represented in the assemblages and most taxa still exist, allowing a direct comparison between past and extant birds associations. Here we analyse the bird remains from the early Pleistocene levels of the Sima del Elefante site (1.1 to 1.5 million years old). Almost 10.000 remains belonging to at least 26 different taxa have been included. The assemblage is dominated by corvids and has a mixed origin, with cave-dwelling taxa dying in the cave and other taxa being accumulated by predators. The Sima del Elefante avian assemblage provides the oldest record of several taxa in the Iberian Peninsula (Haliaeetus albicilla, Corvus pliocaenus). Besides, here we report the oldest evidence of Imperial Eagle in the Iberian Peninsula, prior to the separation of the oriental and Iberian populations. The assemblage composition suggests that open environmental conditions were dominant, with minor presence of woodlands and water bodies, which is congruent with some previous approaches by other proxies. The first humans occupying the Iberian Peninsula inhabited under Mediterranean climate conditions, which gradually deteriorated, as reflected by the avian turnover recorded at the middle Pleistocene Atapuerca assemblages.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions.






