EXPANDING THE RECORD OF LARVAE OF FALSE FLOWER BEETLES WITH PROMINENT TERMINAL ENDS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54103/2039-4942/17084Keywords:
Scraptiidae; Scraptiinae; Baltic amber; Burmite; quantitative morphology; shape analysis.Abstract
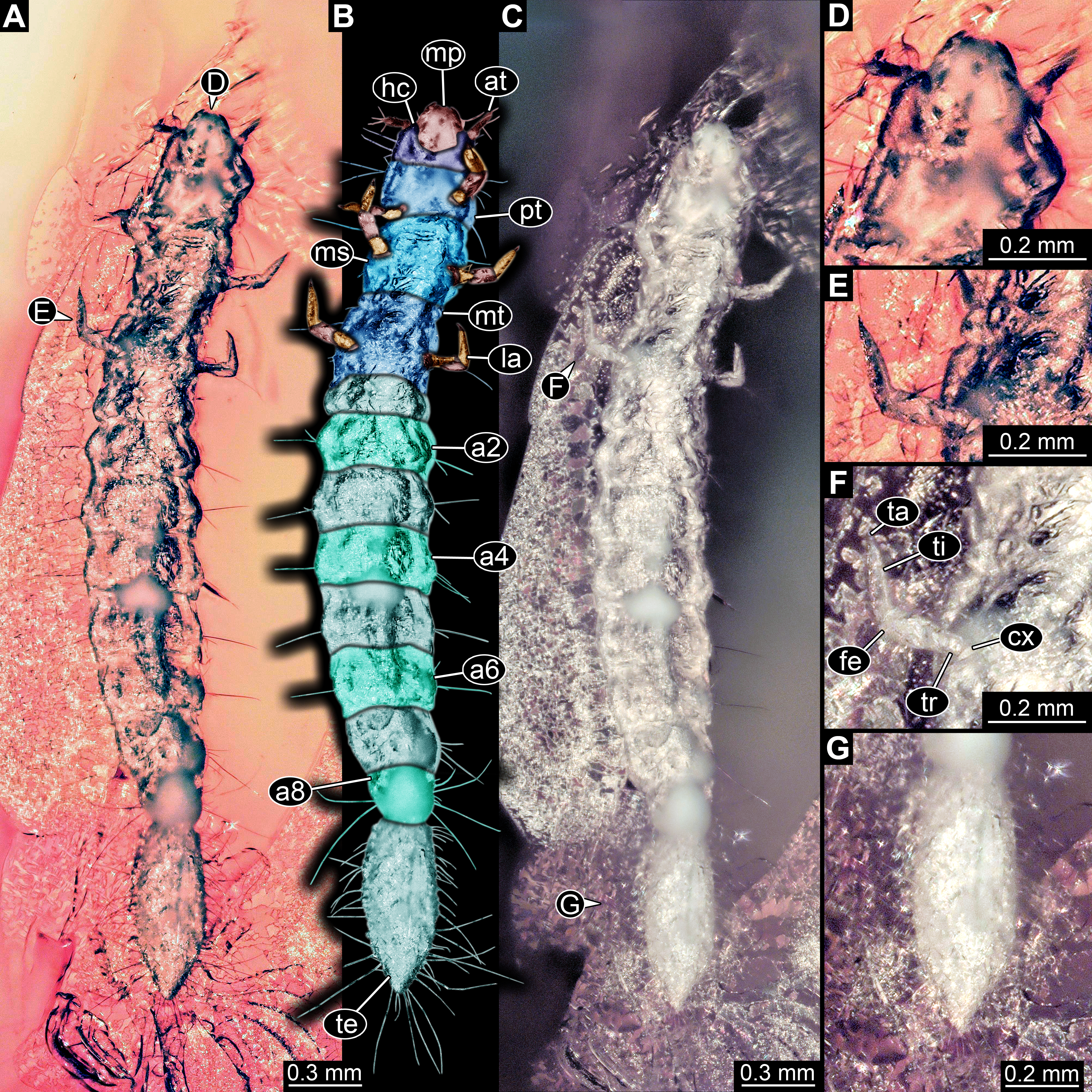
Beetle larvae contribute to the overall biomass with a great share, yet they often stay unnoticed and underexplored. Larvae of the group Scraptiidae, also called false flower beetles, lead a life hidden in the wood, not easily accessible for observers. There, they contribute to wood decomposition and carbon cycling. Even though their ecological role is of great importance, these larvae have been comparably rarely studied. This is true for extant as well as fossil representatives of this group. It seems that this knowledge gap is not based on the limited availability of material but results from insufficiently studied material. Here we report new specimens, of which seven are extant and twelve are fossil. Fossil specimens are either from 40-million-year-old Baltic amber (Eocene) or 100-million-year-old Myanmar amber (Cretaceous), the latter representing the oldest record of these larvae. All specimens considered here possess a large, elongated terminal end. We performed an outline analysis of the shape of this terminal end for all so far known larval specimens sufficiently well preserved (in total 33 specimens: 17 extant, 14 Eocene, 2 Cretaceous). There is a recognisable difference between Eocene and extant specimens, yet it remains unclear whether this is due to different represented larval stages or an effect of evolution.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 ANA ZIPPEL, CAROLIN HAUG, CHRISTEL HOFFEINS, HANS-WERNER HOFFEINS, JOACHIM T. HAUG

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyright without restrictions.






